Sebaceous cyst Removal
Overview
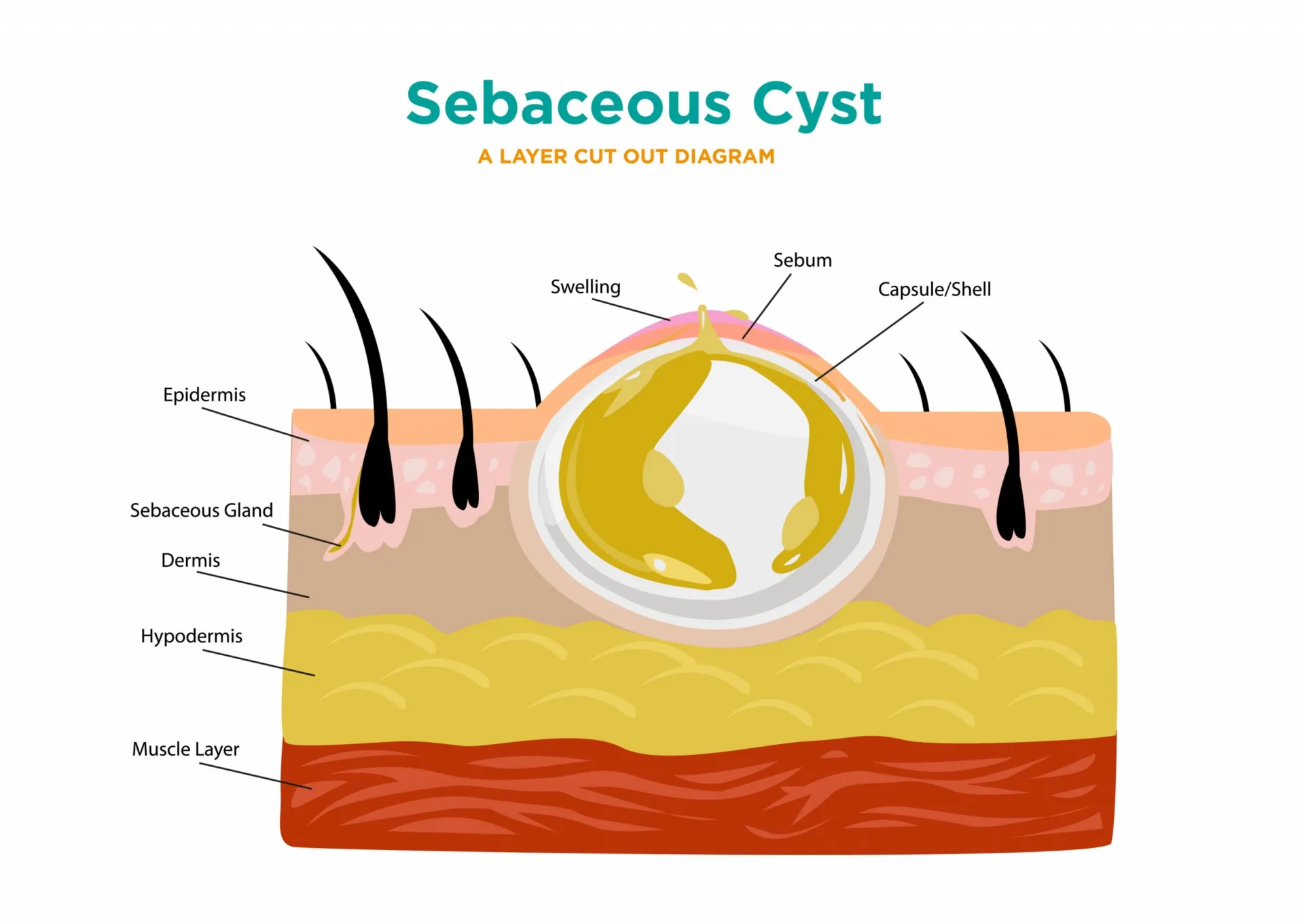
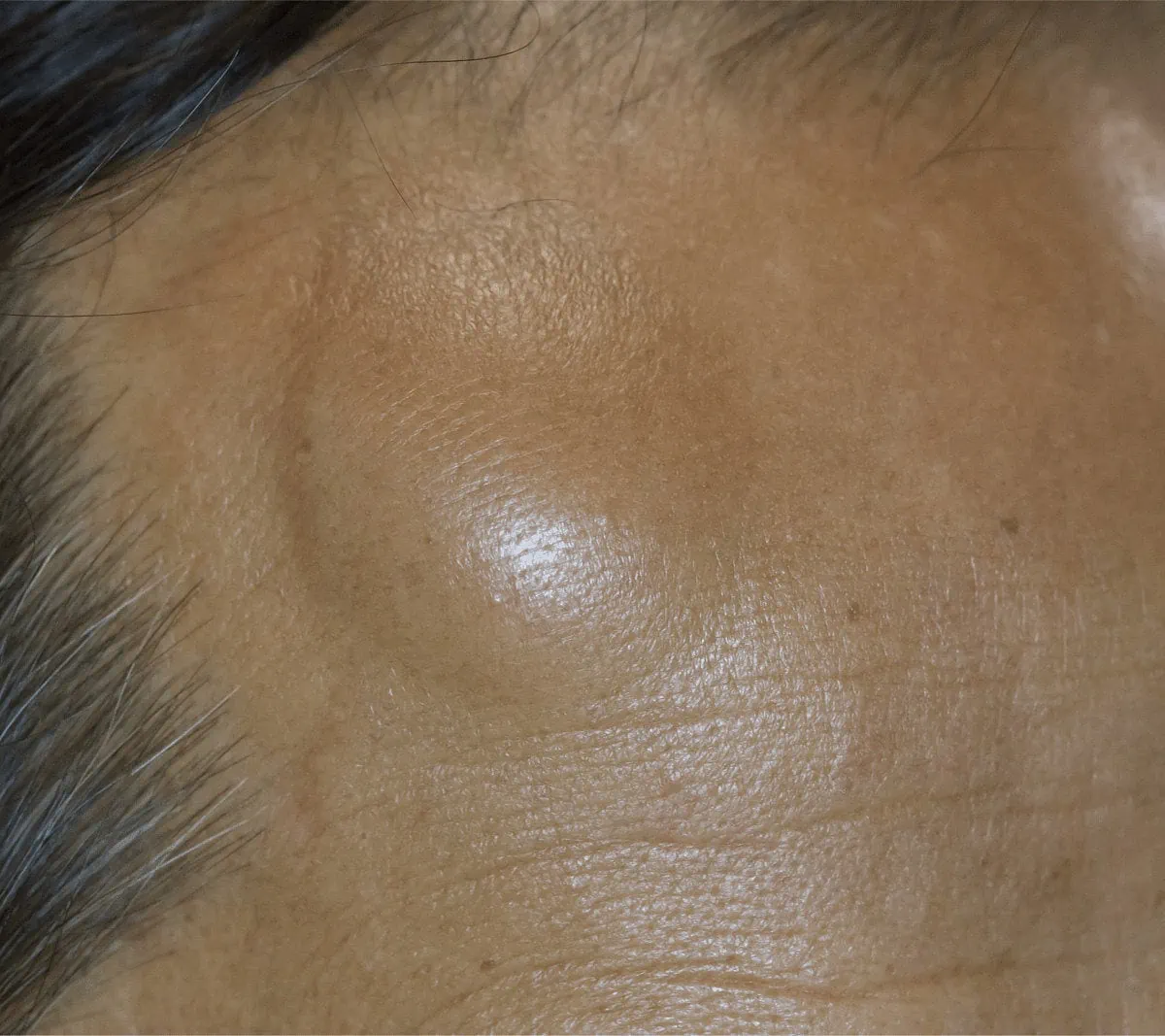
A sebaceous cyst is a round, dome-shaped lump. It’s yellow or white, often with a small dark plug through which you might be able to squeeze out oily secretions or pus. Sebaceous cysts are common and are noncancerous. They are also referred to as Epidermal cysts, Epidermal inclusion cysts and Pilar cysts. Sebaceous cysts are mostly found on the face, scalp, neck, torso and male and female genital areas. They grow slowly and are not life-threatening as such, but they may become uncomfortable and can become infected.
Sebaceous cysts form blocked sebaceous glands. A sebaceous gland produces oily secretion called sebum that coats our hair and skin. Cysts can develop if the gland or its duct, the passage where oil is able to leave,
Call today to arrange a consultation to remove your Sebaceous Cyst
Treatment time
30 – 45min
Recovery time
Immediate
Results duration
Long Lasting Results
Treatment price
From €300
Generally, they are benign painless lumps under the skin, but have the potential to become painful and/or infected. This is best avoided by their removal under local anesthesia.
What is a sebaceous cyst?
A skin cyst is a fluid-filled lump just underneath the skin. A cyst usually is a slow-growing lump that can move easily under the skin. These cysts are closed sacs that can be found under the skin of the entire body (except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet). They affect young and middle-aged adults, and are particularly common in people with acne.
What are the causes sebaceous cysts?
Some of the cells in the top layer of skin produce keratin, a protein that gives skin its strength and flexibility. Normally, these cells move up to the surface of the skin as they start to die so they can be shed. But the cells sometimes move deeper into your skin and multiply, forming a sac. They secrete keratin into the middle of the sac, which forms a thick, yellow paste. Sebaceous cysts may be caused by blocked glands or swollen hair follicles in the skin.
Hence, Sebaceous cysts form out of your sebaceous gland. Cysts develop if the gland or its duct (the passage from which the oil is able to leave) becomes damaged or blocked. This usually occurs due to trauma to the area.
The trauma may be a scratch, a surgical wound, or a skin condition, such as acne. Sebaceous cysts grow slowly, so the trauma may have occurred weeks or months before you notice the cyst.
Other causes of a sebaceous cyst may be :
- malshaped or deformed ducts
- damage to the skin during surgery
- genetic/Familial conditions
What are the symptoms of sebaceous cysts?
Small cysts are typically not painful. Large cysts can range from uncomfortable to considerably painful. Large cysts on the face and neck may cause pressure and pain.
This type of cyst is typically filled with white flakes of keratin, which is also a key element that makes up your skin and nails. Most cysts are soft to the touch.
Areas on the body where cysts are usually found include:
- scalp
- face
- neck
- back
- Genital Area
Typically, the feeling of the lump is unpleasant. In some cases, however, cysts can get inflamed and become painful and tender to the touch. The skin on the area of the cyst may be red and warm. Drainage from the cyst appears greyish-white and cheese-like, and has a foul smell.
A sebaceous cyst may be considered atypical — and possibly cancerous — if it has the following characteristics:
- a diameter that’s larger than 5 centimeters
- a fast rate of reccurrence after being removed
- signs of infection, such as redness, pain, or pus draining out.
Diagnosis Of Sebaceous Cyst :
A sebaceous cyst is often diagnosed after a simple physical examination. If your cyst is atypical, it may require additional tests to rule out possible cancer. You may also need these tests if you wish to have the cyst surgically removed.
Common tests used for a sebaceous cyst include:
- MRI scan, which helps spot atypical characteristics and find the best route for surgery
- Ultrasound scan which identifies the contents of the cyst
- punch biopsy, which involves removal of a small amount of tissue from the cyst for histological diagnosis.
Book Your Consultation
Removal of sebaceous cyst
A sebaceous cyst is treated by surgically removing it under local anesthesia. Usually, when cysts are removed, it is not because they may be dangerous, but rather for cosmetic reasons, being uncomfortable or the possbility of getting infected.
It is important to remember that without surgical removal, your cyst will usually come back, if aspirated. The best treatment is to ensure complete removal through minor surgery under local anesthesia.
Cysts left untreated can become very large and may eventually require surgical removal if they become uncomfortable.
The following procedures are used to remove a cyst:
- Conventional wide excision. This completely removes a cyst.
- Minimal excision. A method that causes minimal scarring but carries a risk that the cyst will return.
After the cyst is removed, we routinely prescribe you an antibiotic to prevent infection. You may need to take an antibiotic alongside pain killers until the healing process is complete.
You may also be given a scar cream to reduce the appearance of a surgical scar.
Outlook of a Sebaceous Cyst :
Sebaceous cysts are generally not cancerous. Cysts left untreated can become very large and may eventually require surgical removal if they become uncomfortable or infected.
In rare cases, the removal site may become infected. If your wound site shows any signs of infection, such as redness and pain, or if you develop a fever, please contact us. Most infections will go away with antibiotics.
Request Consultation

- Pilar Cysts - 8th Feb 2022
- Pilonidal Cyst and Pilonidal Sinus - 6th Feb 2022
- Sebaceous Cyst - 7th Apr 2020
